Fundamentals of Cells (English + Hindi)
(Study Material for Students)
1. Introduction to Cells
1.1 Definition
“A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.” Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life.

1.2 Properties of Cells
- Cell Theory:
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
1.3 Types of Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells (प्रोकैरियोटिक कोशिकाएँ):
- Characteristics: No nucleus, smaller in size, simpler structure.
- Examples: Bacteria, Archaea.
- Eukaryotic Cells(यूकेरियोटिक कोशिकाएं):
- Characteristics: Nucleus present, larger in size, complex structure.
- Examples: Animals, Plants, Fungi, Protists.
2. Cell Structure
2.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure
- Cell Wall (कोशिका भित्ति): Provides shape and protection.
- Plasma Membrane (प्लाज्मा झिल्ली): Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm (साइटोप्लाज्म): Jelly-like substance where cellular activities occur.
- Ribosomes (राइबोसोम): Sites of protein synthesis.
- Nucleus (नाभिक): Region containing the cell’s DNA.
- Flagella and Vili (कशाभिका): Appendages for movement and attachment.

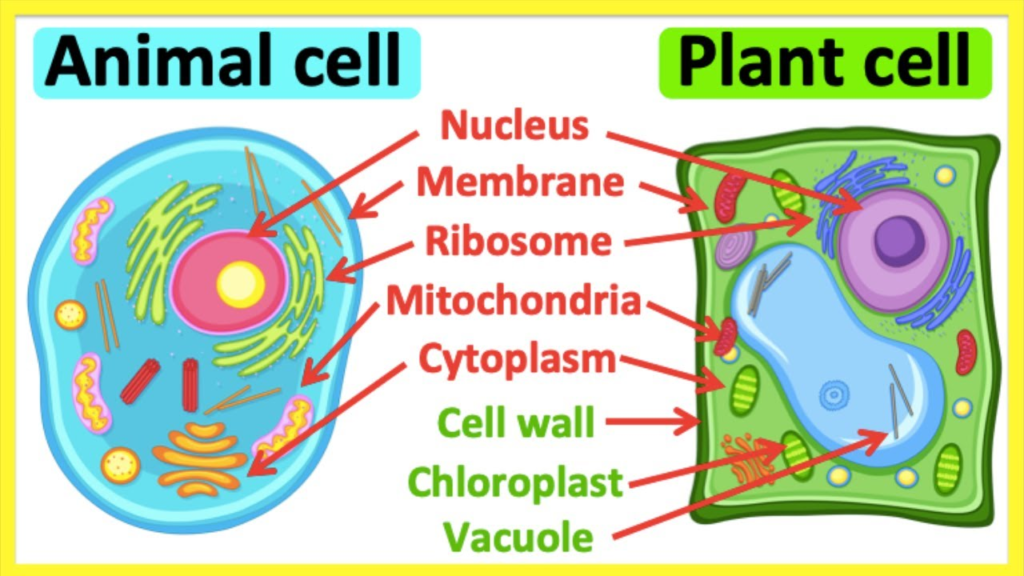
2.2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
2.2.1 Animal Cells
- Plasma Membrane (प्लाज्मा झिल्ली): Semi-permeable membrane controlling substance movement.
- Cytoplasm (साइटोप्लाज्म): Gel-like substance containing organelles.
- Nucleus (नाभिक):
- Nuclear Envelope: Double membrane surrounding the nucleus.
- Nucleolus: Site of ribosome production.
- Chromatin: DNA and protein complex.
- Mitochondria (माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया): Powerhouse of the cell, site of ATP production.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (एंडोप्लाज्मिक रेटिकुलम) (ER):
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins.
- Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes, synthesizes lipids.
- Golgi Apparatus (गोल्गी उपकरण): Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids.
- Lysosomes (लाइसोसोम): Contain digestive enzymes to break down waste.
- Centrioles (सेंट्रीओल्स): Involved in cell division.
Please remember: Animal Cells and Plant Cells are under Eukariotic Cells.!
Download NCERT Chapter on Fundamentals of Cells in English. Click Here.
Download NCERT Chapter on Fundamentals of Cells in Hindi. Click Here.
हिंदी में एनसीईआरटी बुक का चैप्टर डाउनलोड करें
3. Cell Composition
Cell Wall (कोशिका भित्ति)
Definition
- Cell Wall: A rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane in plant cells, fungi, bacteria, and some protists.
Function
- Provides structural support and protection. (संरचनात्मक समर्थन और सुरक्षा प्रदान करता है।)
- Maintains the shape of the cell. (कोशिका के आकार को बनाए रखता है।)
- Prevents excessive water intake. (अत्यधिक पानी का सेवन रोकता है।)
Location
- Found outside the cell membrane in the mentioned organisms.
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) (प्लाज्मा झिल्ली)
Definition
- Cell Membrane: A semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell.
Function
- Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Provides a protective barrier.
- Facilitates communication and signaling between cells.
- कोशिका के अंदर और बाहर पदार्थों की गति को नियंत्रित करता है।
- एक सुरक्षात्मक अवरोध प्रदान करता है.
- कोशिकाओं के बीच संचार और सिग्नलिंग की सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
Cytoplasm (साइटोप्लाज्म)
Definition
- Cytoplasm: The jelly-like substance within the cell membrane, excluding the nucleus.
Function
- Contains all cellular organelles.
- Site of numerous cellular processes, including metabolic pathways like glycolysis.
- Provides a medium for the movement of molecules within the cell.
- इसमें सभी सेलुलर अंग शामिल हैं।
- ग्लाइकोलाइसिस जैसे चयापचय मार्गों सहित कई सेलुलर प्रक्रियाओं का स्थल।
- कोशिका के भीतर अणुओं की आवाजाही के लिए एक माध्यम प्रदान करता है।
Nucleus (नाभिक)

Definition
- Nucleus: The membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material (DNA).
Function
- Controls cellular activities by regulating gene expression.
- Stores genetic information necessary for cell growth, reproduction, and function.
- Site of DNA replication and RNA transcription.
- जीन अभिव्यक्ति को विनियमित करके सेलुलर गतिविधियों को नियंत्रित करता है।
- कोशिका वृद्धि, प्रजनन और कार्य के लिए आवश्यक आनुवंशिक जानकारी संग्रहीत करता है।
- डीएनए प्रतिकृति और आरएनए प्रतिलेखन की साइट।
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Definition
- DNA: The molecule that carries the genetic instructions for life.
Function
- Encodes the information required for the synthesis of proteins.
- Guides development, functioning, and reproduction of living organisms.
- Enables hereditary transmission of traits.
- प्रोटीन के संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक जानकारी को एनकोड करता है।
- जीवित जीवों के विकास, कामकाज और प्रजनन का मार्गदर्शन करता है।
- लक्षणों के वंशानुगत संचरण को सक्षम बनाता है।
Location
- Primarily located in the nucleus (eukaryotic cells) or nucleoid (prokaryotic cells).
- Also found in mitochondria (mitochondrial DNA) and chloroplasts (chloroplast DNA).
Mitochondria (माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया)

Definition
- Mitochondria: Double-membrane-bound organelles known as the powerhouse of the cell.
Function
- Site of cellular respiration and ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production.
- Converts energy from nutrients into usable cellular energy.
- Regulates metabolic processes and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
- सेलुलर श्वसन और एटीपी (एडेनोसिन ट्राइफॉस्फेट) उत्पादन का स्थल।
- पोषक तत्वों से ऊर्जा को उपयोगी सेलुलर ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करता है।
- चयापचय प्रक्रियाओं और एपोप्टोसिस (क्रमादेशित कोशिका मृत्यु) को नियंत्रित करता है।
Ribosomes (राइबोसोम)
Definition
- Ribosomes: Small, non-membrane-bound structures responsible for protein synthesis.
Function
- Translate mRNA (messenger RNA) into polypeptide chains (proteins).
- Found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- एमआरएनए (मैसेंजर आरएनए) को पॉलीपेप्टाइड श्रृंखला (प्रोटीन) में अनुवाद करें।
- प्रोकैरियोटिक और यूकेरियोटिक दोनों कोशिकाओं में पाया जाता है।
Endoplasmic Reticulum (एंडोप्लाज्मिक रेटिकुलम) (ER)

Definition
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: A network of membranous tubules and sacs (cisternae) involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Types
- Rough ER (RER):
- Studded with ribosomes on its surface.
- Synthesizes and processes proteins.
- Transports proteins to the Golgi apparatus.
- Smooth ER (SER):
- Lacks ribosomes.
- Synthesizes lipids and steroids.
- Detoxifies chemicals.
- Stores calcium ions.
4. Cell Function
- Cellular Metabolism
- Cellular Respiration
- Photosynthesis
5. Examples of Cells-
5.1 Animal Cells

- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Part of the immune system, defending against infections.
- Neurons: Transmit nerve impulses for communication within the nervous system.
- Muscle Cells (Myocytes): Responsible for contraction and movement.
- Epithelial Cells: Form the lining of surfaces and cavities in the body.
- Adipocytes: Fat cells, store energy in the form of lipids.
- Osteocytes: Bone cells that maintain bone tissue.
- Hepatocytes: Liver cells, involved in metabolism and detoxification.
5.2 Plant Cells
- Parenchyma Cells: Fundamental tissue of plants, involved in photosynthesis and storage.
- Collenchyma Cells: Provide support and flexibility to growing parts of plants.
- Sclerenchyma Cells: Provide strength and support, have thick, lignified walls.
- Guard Cells: Regulate the opening and closing of stomata for gas exchange.
- Xylem Cells: Conduct water and nutrients from roots to the rest of the plant.
- Phloem Cells: Transport sugars and other metabolic products throughout the plant.
- Fungal Cells
- Yeast Cells (Saccharomyces cerevisiae): Used in baking and brewing.
- Mold Cells (Aspergillus, Penicillium): Decomposers and producers of antibiotics.
- Protist Cells
- Amoeba: Single-celled organisms that move and feed by pseudopodia.
- Paramecium: Ciliated protists that feed on microorganisms.
- Euglena: Photosynthetic protists with flagella for movement.
- Plasmodium: Causes malaria, transmitted by mosquitoes.
5.3 Bacteria
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): Commonly found in the intestines of humans and animals.
- Staphylococcus aureus: Found on the skin and in the respiratory tract; can cause infections.
- Bacillus subtilis: Soil bacterium used in research and industrial applications.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Causes tuberculosis.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: Causes pneumonia and other respiratory infections.
Download NCERT Chapter on Fundamentals of Cells in English. Click Here.
Download NCERT Chapter on Fundamentals of Cells in Hindi. Click Here.
हिंदी में एनसीईआरटी बुक का चैप्टर डाउनलोड करें

Really it’s soo informative and well explained… 🌸🌸
Nice content 📕