(Study Material For DNL Students/ other Paramedical Students)
What is Muscular Tissue
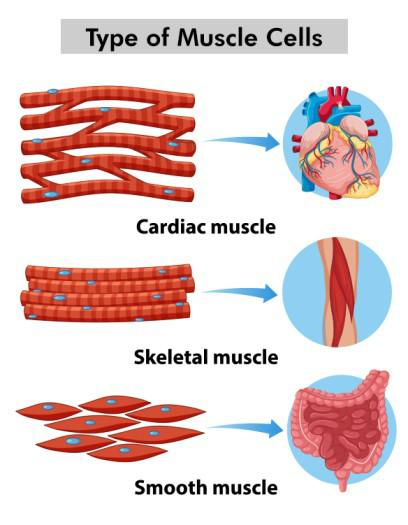
Muscle tissue (Myocytes) is specialized for contraction, enabling movement and force generation. It is categorized into three types: skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones and facilitates voluntary movements; cardiac muscle, which makes up the heart and pumps blood; and smooth muscle, which is found in the walls of internal organs and controls involuntary movements. Each type has distinct structural and functional characteristics suited to its specific role.
The primary functions of muscle tissue include generating movement, maintaining posture and body position, and producing heat through muscle contractions. Muscle tissue is also essential for various bodily functions, such as circulation, digestion, and respiration, by enabling the contraction and relaxation of muscles in the heart, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory system.
Types of Muscular Tissue
- Skeletal Muscle
- Smooth Muscle
- Cardiac Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Also called- Striated Muscles
Skeletal muscle is a type of striated muscle tissue that is primarily responsible for voluntary movements of the body. It is characterized by long, cylindrical cells with multiple nuclei located at the periphery and a striated appearance due to the organized arrangement of actin and myosin filaments. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones via tendons, and its contraction generates the force required for movements such as walking, lifting, and facial expressions. This muscle type is under conscious control and plays a crucial role in maintaining posture, stabilizing joints, and generating body heat.
Smooth Muscle
Also called- Striped Muscles or Non-Striated Muscles
Smooth muscle is a type of non-striated, involuntary muscle tissue found in the walls of internal organs and structures such as the digestive tract, blood vessels, and the bladder. The cells are spindle-shaped, have a single centrally located nucleus, and lack the striations seen in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle contraction is regulated by the autonomic nervous system and various local factors, allowing for the control of internal processes such as peristalsis in the intestines, vasoconstriction, and the regulation of blood flow. This muscle type is essential for involuntary functions that maintain homeostasis within the body.
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle is a specialized type of striated muscle found exclusively in the heart. It features cells that are short, branched, and interconnected through intercalated discs, which facilitate synchronized contractions of the heart. The cells typically have a single, centrally located nucleus, and the striated appearance is due to the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments similar to skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscle operates involuntarily and is regulated by the autonomic nervous system and intrinsic pacemaker cells within the heart. Its primary function is to pump blood throughout the body, maintaining circulation and delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
